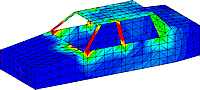
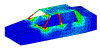
 Currents Flowing On A Vehicle With Antenna Located Inside The Vehicle. Currents Flowing On A Vehicle With Antenna Located Inside The Vehicle. |
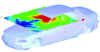 Near-Fields Inside An Automobile With Antenna In Rear View Mirror Near-Fields Inside An Automobile With Antenna In Rear View Mirror |
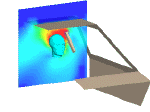 Currents Flowing On A Person With An Antenna Located Inside The Vehicle Currents Flowing On A Person With An Antenna Located Inside The Vehicle |

The phone holder shown in the images is designed to be placed on the dashboard of a car and hold a smartphone in a way that the rear of the phone faces towards the windshield. This design could be beneficial in reducing the exposure of passengers to radiofrequency radiation emitted by the phone. When a phone is in use, especially for data-heavy tasks or when the signal is weak, it can operate at higher power levels. By orienting the phone so that the rear, which is typically the main source of radiofrequency radiation emission, is directed away from the interior of the car, the design aims to minimize the amount of radiation that reflects back into the passenger compartment.
This approach takes into account the principle that electromagnetic radiation, including the microwave frequencies used by cell phones, can reflect off surfaces like the glass and metal inside a car, potentially leading to a higher cumulative exposure for the passengers. By directing the radiation outwards through the windshield, which generally does not reflect microwaves as strongly as metal, the holder could help in reducing this effect.
However, it’s important to note that the level of exposure reduction would depend on various factors, including the specific phone model, the strength of the cellular signal, and the materials used in the car’s interior.
Often you will take your cell phone into different environments, some of which, like small metal-enclosed areas, affect the operation of your cell phone. These environments often cause the cell phone to operate at its highest power output levels and can amplify EMF power densities surrounding the cell phone user.
This Environment includes Cars, Buses, Motor Homes, and any other place you find yourself inside and in close proximity to conductive walls that reflect microwave emissions.
Simply put, conductive surroundings act as concentrating reflectors like the cooking cavity of a microwave oven. When inside a metal enclosure, Radio Frequency Radiation (RFR) gets trapped inside the conductive walls creating what is scientifically called a “Faraday Cage”
The Faraday Cage was named after the man who discovered it, Dr. Michael Faraday (1791-1867). Dr. Faraday is known as the inventor of modern EMF (Electromagnetic Field) principles.
The Faraday Cage Effect means that the electric charge on a conductor sits on its outer surface, demonstrating that radio waves cannot penetrate a Faraday cage by creating a charged reflective barrier blocking RF radiation.
The Bottom Left Picture shows RF radiation trapped in a car when the transmitting antenna is located inside the car. The Bottom Right Picture shows how easily the RF hazard can be eliminated by using a Hard Wired External Antenna – which isn’t available anymore because manufacturers removed the antenna ports on phones!