Smartphones Irradiate the Thyroid: Tumors Continue To Surge
Introduction
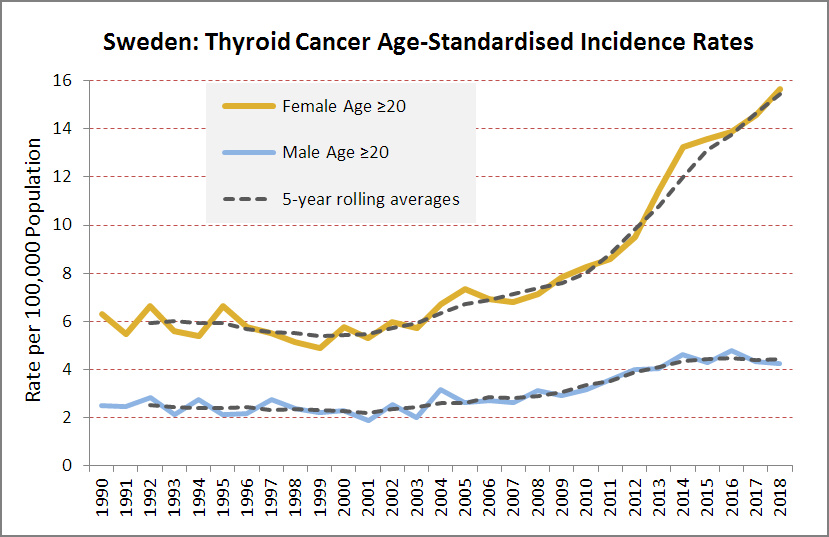
Thyroid cancer among women is skyrocketing globally, with incidence growing faster than any other cancer. Despite being aware of this alarming trend for years, the reasons behind it remain elusive. While overdiagnosis due to improved screening tools is often cited, emerging evidence suggests other contributing factors, including the radiation from smartphones. This blog post will delve into these potential risks and explore recent studies that have highlighted the dangers posed by modern technology.
Rising Thyroid Cancer Rates: A Closer Look
Thyroid cancer rates have been increasing steadily, particularly among women. The prevailing view is that enhanced diagnostic tools, such as ultrasound, have led to an “epidemic of diagnosis,” where many small tumors, which would likely never pose a real threat, are now being detected. Despite this, thyroid cancer remains one of the most survivable cancers, with a 98-99% five-year survival rate. However, the role of environmental factors, such as radiation exposure, cannot be ignored.
Credits Microwave News on the impact of smartphone radiation on thyroid health.
The Role of Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Radiation
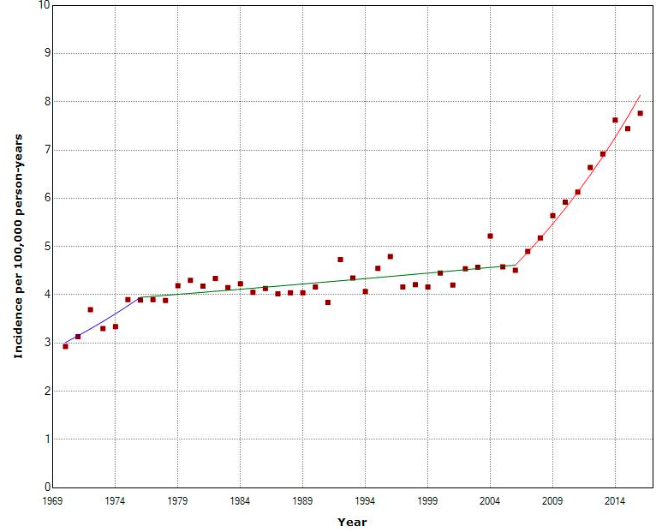
Ionizing radiation, like that from X-rays, is a known cause of thyroid cancer, particularly with a short latency period. However, non-ionizing radiation (NIR) from smartphones and Bluetooth devices is also coming under scrutiny. In 2016, Swedish researchers Michael Carlberg and Lennart Hardell suggested that RF/microwave radiation from cell phones could be a risk factor for thyroid cancer. They highlighted that the antenna in smartphones, when held up to the ear, irradiates the thyroid directly.
Recent Findings and Ongoing Research
A pivotal study by Yawei Zhang at the Yale School of Public Health, published in 2018, initially found no significant elevation in tumor rates. However, an updated analysis incorporating genetic information revealed that individuals with certain DNA repair gene variants had a five-fold increased risk of tumors with prolonged cell phone use. This finding underscores the potential susceptibility of individuals to RF radiation based on their genetic makeup.
Additionally, the Swedish Cancer Registry’s latest data shows a continuous spike in thyroid cancer rates, particularly among women, suggesting that something more than better detection is at work. This is further corroborated by the fact that large tumors, which would likely have been detected without advanced screening tools, are also on the rise.
Bluetooth Headsets and Thyroid Health
A recent study, “Epidemiological Exploration of the Impact of Bluetooth Headset Usage on Thyroid Nodules using Shapley Additive Explanations Method,” published in Scientific Reports on June 21, 2024, highlights the risks associated with prolonged Bluetooth headset use. The study found that frequent use of Bluetooth headphones is strongly linked to an increased risk of developing thyroid nodules, potentially due to the cumulative effects of NIR emitted by the devices on the thyroid gland.
What Does This Mean for You?
These findings raise serious concerns about the long-term health impacts of everyday devices. Given the potential risks, it is crucial to take proactive measures to protect yourself:
- Limit Bluetooth Usage: Reduce the duration and frequency of Bluetooth headset use.
- Use Alternatives: Opt for air tube headsets or speakerphone options whenever possible.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest research and updates on the health impacts of RF radiation.
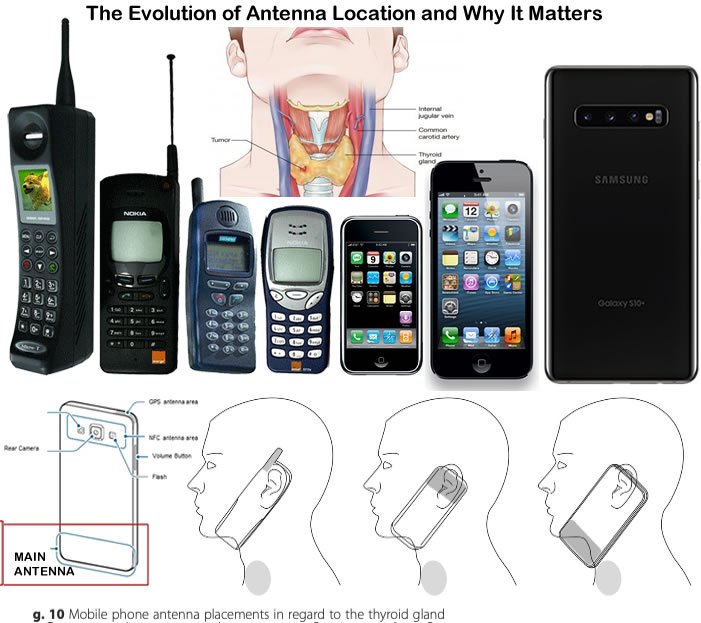
Conclusion
As the evidence mounts, it is becoming increasingly clear that the radiation emitted by smartphones and Bluetooth devices may pose significant health risks. The dramatic rise in thyroid cancer rates, coupled with studies linking RF radiation to tumor development, underscores the need for updated safety guidelines and continued research. By staying informed and taking precautionary measures, we can mitigate these risks and protect our health.